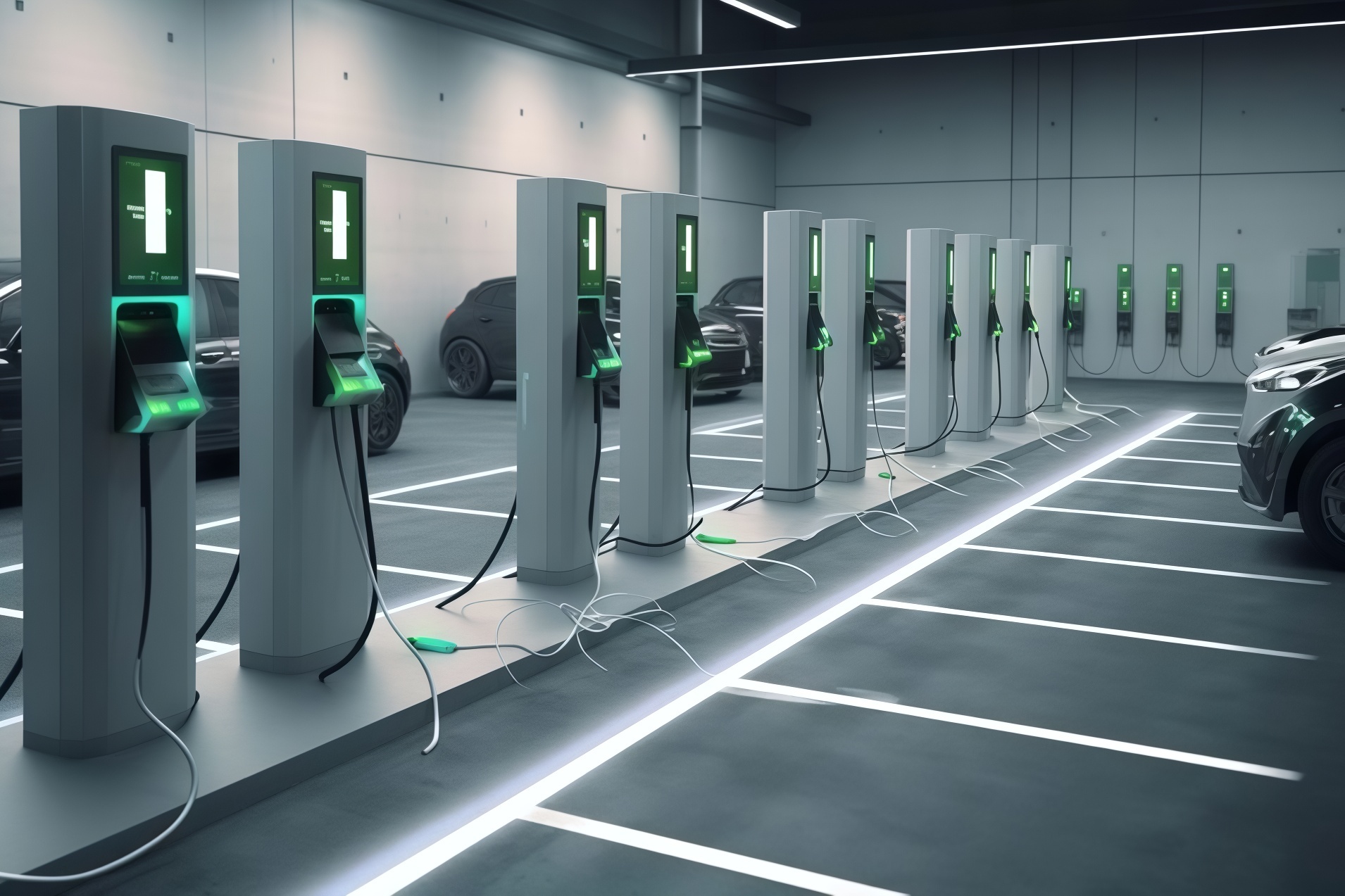
Chinese companies’ persistence in pursuing the European market is grounded not only in its commercial potential but also in Europe’s advanced policies and demand for environmental protection and new energy vehicles.
However, this endeavour is not without its challenges. EU tariff measures could increase the cost of Chinese electric vehicles, undermining their competitiveness in the European market. In response, Chinese companies may need to adopt diversified strategies, including negotiating with the EU, adjusting pricing strategies, investing in local manufacturing facilities within Europe to circumvent high tariffs, and exploring markets in other regions.
Concurrently, divisions exist within the EU regarding the imposition of tariffs on Chinese electric vehicles. Some member states, such as Germany and Sweden, abstained from voting, while Italy and Spain expressed support. This divergence creates room for further negotiations between China and the EU, allowing China to explore possibilities for tariff reductions while preparing to counter potential trade protectionist measures.
In summary, although Chinese new energy vehicle enterprises face certain challenges in the European market, they still have opportunities to maintain and expand their operations in Europe through multiple strategies. Concurrently, the Chinese government and enterprises are actively seeking solutions to protect their interests and advance Sino-European cooperation in the new energy vehicle sector.
Post time: Sep-13-2025

 Portable EV Charger
Portable EV Charger Home EV Wallbox
Home EV Wallbox DC Charger Station
DC Charger Station EV Charging Module
EV Charging Module DC Charging Connector
DC Charging Connector EV Accessories
EV Accessories

