Main classification and certification standards of European charging pile suppliers
According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA): “In 2023, approximately US$2.8 trillion will be invested globally in energy, with over US$1.7 trillion directed towards clean technologies including renewable energy, electric vehicles, nuclear power, grids, storage, low-emission fuels, efficiency improvements and heat pumps. The remaining sum, slightly exceeding US$1 trillion, will be allocated to coal, gas and oil. Solar energy expenditure surpassed upstream oil for the first time. Driven by renewables and electric vehicles, annual clean energy investment is projected to grow by 24% between 2021 and 2023, compared to 15% growth for fossil fuels over the same period. Over 90% of this growth stems from developed economies and China, indicating governments are placing greater policy emphasis on renewable energy. Analysis indicates that over 90% of global electricity growth over the next five years is projected to come from renewables, with renewable energy expected to surpass coal as the primary global power source by early 2025. By 2025, the global number of electric vehicle charging points is projected to exceed 120 million, with fast-charging points surpassing 4 million. This forecast indicates that as electric vehicle sales grow, charging infrastructure will receive increased investment and development. Governments worldwide will also promote the development of electric vehicles and charging infrastructure through policy support and funding to address climate change and reduce vehicle emissions.
Guohai Securities’ ‘Charging Station Industry In-Depth Report’ reveals: New energy vehicle penetration in Europe is accelerating rapidly. In 2021, Europe’s new energy vehicle penetration rate reached 19.2%, while the ratio of public charging stations to vehicles stood at 15:1, indicating a significant charging infrastructure gap. According to IEA statistics, Europe’s new energy vehicle stock stood at 5.46 million units in 2021, with 356,000 public charging points, corresponding to a vehicle-to-charger ratio of 15.3:1. As new energy vehicles accelerate their penetration in Europe, with a target public vehicle-to-charger ratio of 13:1 set for 2025, the European new energy vehicle stock is projected to reach 17.5 million units by 2025. Public charging points are projected to reach 1.346 million units, corresponding to annual sales volumes of 210,000, 222,000, and 422,000 units for the years 2023-2025 respectively, representing a compound annual growth rate of 50.1%.
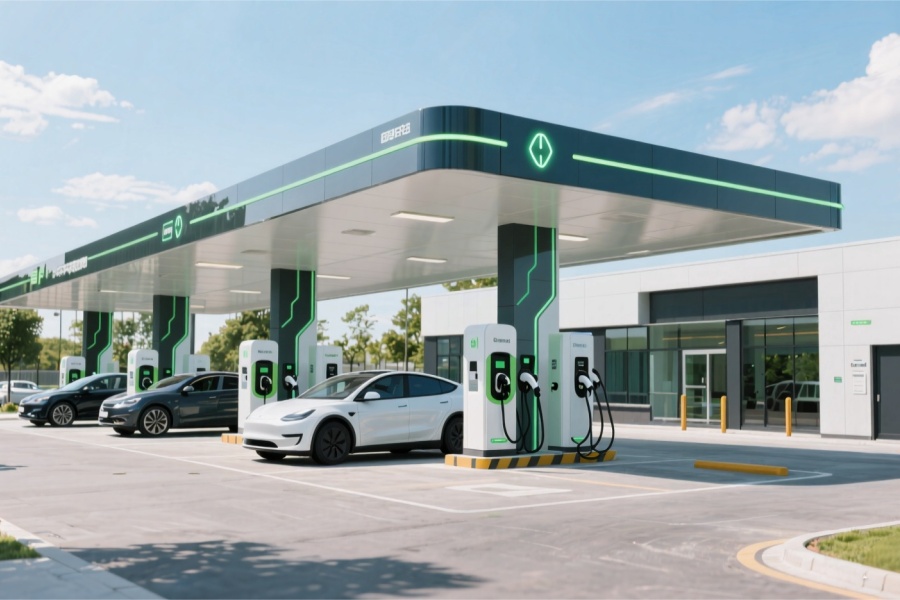

European charging point suppliers primarily fall into four categories: traditional energy giants, large integrated electrical companies, new energy vehicle manufacturers, and specialised charging point operators. Traditional energy giants such as BP and Shell are accelerating the transition of their conventional petroleum businesses towards new energy ventures through acquisitions of charging station operators. Large integrated electrical companies, notably ABB, Siemens, and Schneider Electric, focus on manufacturing charging equipment and currently dominate the European charging point market. New energy vehicle manufacturers, exemplified by Tesla and IONITY, primarily support their electric vehicle fleets through charging infrastructure; specialised charging operators, such as North America’s ChargePoint and Europe’s EVBox, not only supply charging points but also provide subsequent software and service offerings, promoting charging software business models.
Overseas charging standards and certifications present greater complexity. Currently, five primary charging standards exist internationally: China’s national standard GB/T, the American CCS1 standard (Combo/Type 1), the European CCS2 standard (Combo/Type 2), Japan’s CHAdeMO standard, and Tesla’s proprietary charging interface standard. Globally, the CCS and CHAdeMO standards see the widest adoption, supporting a greater variety of vehicle models. Concurrently, overseas automotive testing standards and regulations are comparatively more stringent than those within the Chinese market.
Post time: Sep-13-2025

 Portable EV Charger
Portable EV Charger Home EV Wallbox
Home EV Wallbox DC Charger Station
DC Charger Station EV Charging Module
EV Charging Module DC Charging Connector
DC Charging Connector EV Accessories
EV Accessories
